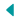
Fiber optic cable is a network cable that, in comparison with other traditional metal patch cords, is offering better bandwidth and data carrying. The information is transferred via pulses of light which pass through transparent glass or plastic strands. These pipes are surrounded by a layer of cladding which is also made in plastic or glass, but with a different density than the inner strand. The cladding is wrapped in a buffer tube and an outer jacketing.
About how they work and why are they needed can be read bellow.
What are the fiber optic cables made of and how do they work?
As we slightly mentioned before, the core strands are made of a combination of glass (silica) and/or plastic. These materials not only ensure a high level of performance, but also offer high flexibility, lighter weight, and better resistance to shock and bending. And while the strands are the central system that ensures the good functionality of a cable, there are other multiple components that play an important role in the transfer of data through the fiber optics.
Light is used to transmit data pulses along the strands at the core of the cable. The light is created by either a laser or a LED source. An input signal coming from the transmitter is received and it is converted into light pulsations before bouncing it along the fiber core.
The fibers are surrounded by an additional cladding layer which has a different refractive index than the core strands. These differences between cladding and fibers allow the light pulses to bend at specific angles as they travel along the length of the cable.
The reflective properties of the light bound the light pulses within the transparent parts of the fiber cable. The light pulses move in a zigzag pattern along the full run length of the fiber optics. In the case of particularly long cable runs, in order to keep enough signal strength, they will need to convert back and forth between electrical signals and light pulses, at several points along the way. This process can be done with the help of repeaters, additional internal components.
The light signals travel at around 70% the speed of light most of the way and once they reach the destination, the can be interpreted as data and converted to output by a piece of receiving equipment.
Types of fiber optic cables
There are two types of cables that are commonly used: Single mode and Multimode.
Single mode cables are designed to carry light directly down the fiber. It is a single strand of glass fiber and has a diameter of 8.5-10 microns. Because it has one mode of transmission, it will propagate 1310 or 1550 nm.
Compared to the multimode fiber, the single mode patch cords carry a higher bandwidth, but it requires a light source with a narrow spectral width. The single mode gives a higher transmission and up to 50 times more distance than the multimode. The core from a single mode cable is smaller than one from a multimode.
Single mode is a vital part of broadband networks. It designed to transmit data over long distances, thus making it perfect for cable television networks or college campuses.
Multimode patch cords have
a bigger diameter, typically 50-100 microns for the light carry component. Over
medium distances, multimode fibers give high bandwidths at high speeds. Light
waves are dispersed into numerous paths, or modes, as they travel through the
cable’s core typically 850 or 1300nm.
In cable runs longer than 914,4 meters, the multiple cable pats can cause distortion at the receiving end, resulting in an unclear and partial data transmission.
Multimode cables are considered to be the “domestic” fiber as they are used for local-area network, as an example, they can be used in FTTH. Multimode can reach up to 100Gbps Ethernet.
PeakOptical Multimode fiber portfolio includes OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5.
Characteristics of fiber optic cables
Transmission speeds: the data transfer rates depend mainly on the mode of the cable. As mentioned above, fiber optic can be either single mode or multimode and these deliver higher or lower speeds over specific distances. Fiber optic offers the fastest mode of network connectivity and data transfer available on today’s market. Still, new types of fiber optic are constantly developing. In 2018, NICT Network System Research Institute and Fujikura Ltd went public as having developed ‘a 3-mode optical fiber, capable of wide-band wavelength multiplexing transmission with standard outer diameter (0.125 mm) that can be cabled with existing equipment’. (phys.org)
The PROs of fiber optic cables
These days, everyone is talking about the advantages of setting up a fiber optic network for your business instead of copper cabling. While it is clear that both offer benefits, more often than not, fiber optic turns out to be the most advantageous choice..
FIBER OPTICS IS CONSIDERABLY FASTER
Is there anyone who still doesn’t know that fiber optic is a lot faster than copper? While it is true that copper networks perform just fine and are able to deliver acceptable speeds that satisfy the demands of most small business, once you go fiber, you can never go back. Fiber optic is able to transmit data way faster, over greater distances, without slowing down or altering the quality of the information in any way.
FIBER OPTIC CABLES COVER LONG DISTANCES
As we shortly mentioned earlier, not only that fiber optic transmits data quicker, it can actually do it over longer distances, compared to copper. Because of its low power loss, the signals can be transmitted over long distances without any trouble.
YOUR DATA IS SAFE
Any business owner has that small though at some point – what if someone is stealing my data? No worries! That will not be a problem with fiber optic cables, as they put a very low-security risk. You cannot actually see how the information is being transmitted, making it, in this way, harder to access.
ONE OF THE GREATEST ADVANTAGES: THEY ARE WILDLY AVAILABLE
At the beginning of fiber optic technology, the main issue was that the fiber optic cables were not that easy to find and were considerably pricier than copper products, which were (and still are) easily accessible. With the development and growth of fiber optic market, the fiber optic products are now available for everyone, everywhere.
If you are in need of fiber optic components, do not hesitate to check PeakOptical’s portfolio of products and contactour team for assistance.
Info source: RS