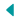
Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) is the technology that enables the transmission of large amounts of data between two sites. This technique increases bandwidth by allowing two or more light wavelengths (or colors of light) to travel on a single optical fiber.
Two types of WDM
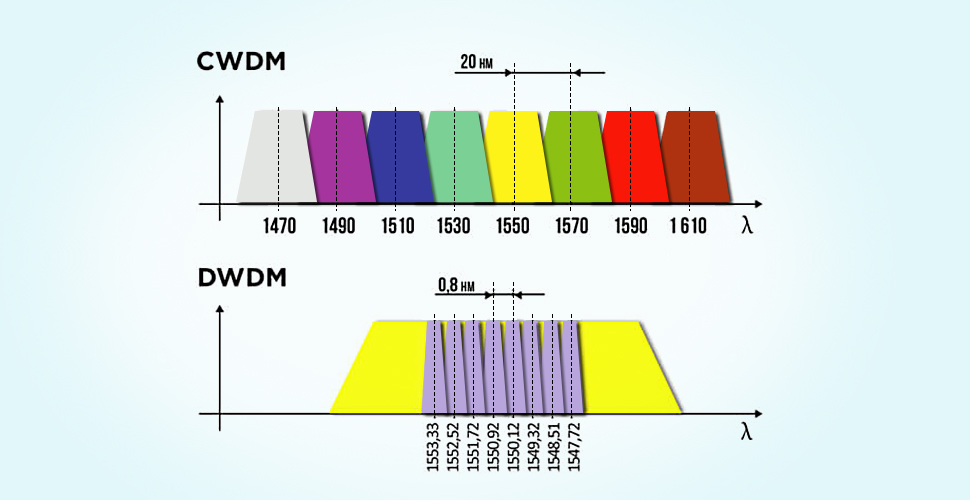
Picture source: FS.com
- Coarse Wave Division Multiplexing (CWDM) – are systems designed for short-range communications. The transmission of data is realized using 18 channels with wavelengths of 1270 1610 nanometers (nm). The channel spacing is 20 nm, the channel itself is 13 nm, and the remaining 7 nm are meant to secure the space to the next channel. The CWDMs are advantageous if spectral efficiency is not essential.
- Dense Wave Division Multiplexing (DWDM) – are designed for long-haul transmission. These systems make it possible for up to 80 separate wavelengths or channels of data to be transmitted on a single optical fiber.
PeakOptical CWDM and DWDM solutions open countless opportunities to scale broadband environments where the number of fibers might create limitations. You can check our products here.
*This post marks the beginning of the series ”PeakOptical Fiber Optic Definitions”. The articles that are to come have the purpose of explaining general terms used in the field of fiber optics.